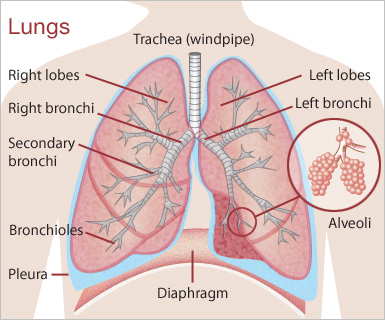
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a common form of cancer and mainly occurs in the tissues of the lung and in the cells that line the main airway (bronchus). It can also develop in the windpipe (Trachea). There are two main forms of lung cancer, which are Small Cell Lung Cancer and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
Non-Small Cell comprises of squamous cell, adenocarcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. Together, these account for almost 90% of all lung cancer cases.
Squamous cell lung cancer is the most common form of primary lung cancer and develops from the cells of the main airways. It is most often found in the center of the lung in one of the main airways.
Around 40% of non-small cell lung cancers are adenocarcinoma, which begins on the outside surface of the lung. This form is also more likely to spread (metastasize) to lymph nodes and other organs.
Around 10% of lung cancers are large cell. This form of lung cancer usually spreads quite quickly.
In many cases, lung cancer may also spread to other organs including the brain, adrenal glands, liver or bones and cause other symptoms that prompt seeking a medical evaluation.
What are the Signs and Symptoms Of Lung Cancer?
In its early stages, lung cancer produces few symptoms and you may not be aware that you have it. At more advanced stages there are many symptoms that you may experience.
These may include:-
- Coughing or wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up phlegm which has blood in it
- Aches or pains when breathing
- A loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Other less common symptoms may include:-
- Difficulty when swallowing
- A hoarse voice
- Swelling of the face
- A persistent ache or pain in the chest region
- Swelling in the neck (Enlarged lymph nodes)
Causes and Risk Factors for Lung Cancer
The most common risk factor for lung cancer is smoking, which is thought to be responsible for around 8 out of 10 cases. The main risk factors are:-
- Smoking
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Chemical exposure – Exposure to Asbestos, silica, diesel exhaust, arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, vinyl chloride, coal products, mustard gas, chloromethyl ethers and chromium compounds.
- Air pollution
- Family History – If you have a close relative with lung cancer, you are slightly more at risk of developing it yourself
- Radiotherapy – Previous radiotherapy treatment for breast cancer and Hodgkin lymphoma increases the risk of lung cancer
- Previous lung disease – Those who have previously had a lung disease such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, emphysema or bronchitis have an increased risk
- Weakened immune system – If you have HIV or AIDS you are 3 times more likely to get lung cancer due to a weakened immune system
- Radon – Exposure to Radon gas can increase your risk of lung cancer
Recommended Protocol for Lung Cancer
For further information on available protocols, please see our recommended lung cancer program page.