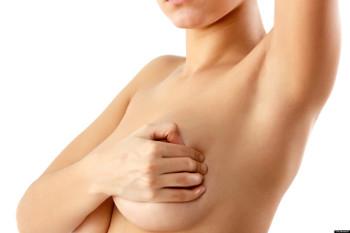
What is Breast Cancer?
Cancer that forms in tissues of the breast, usually the ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple) and lobules (glands that make milk), is called Breast Cancer.
Breast cancer can occur in both men and women, although incidents of male breast cancer are much are less common. It is thought that around 10% of women in the West will be affected by breast cancer at some point during their lifetime.
Although early detection of breast cancer has improved somewhat, it remains that around 20% of women with breast cancer will die from the disease. Breast cancer is the second most common type of cancer that causes death among women.
The probability of breast cancer rises with age, but breast cancer tends to be more aggressive when it occurs in younger women. Most cases of breast cancer occur in the over 50s and those who have been through menopause.
A form of cancer that occurs more in younger women (although rare) is inflammatory breast cancer. This is where the breasts become inflamed and is due to a blockage in small lymph channels in the breast.
It can be difficult to spot because a lump does not appear and therefore not often detected by mammography or ultrasound. Inflammatory breast cancer is sometimes initially misdiagnosed as a breast infection like mastitis.
Other forms of breast cancer include Pagets Disease, DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma in Situ), LCIS (Lobular Carcinoma in Situ), Invasive Ductal and Invasive Lobular.
Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer
The most common symptoms of breast cancer may Include:-
- Itching in the armpit or around the breast region
- Swelling or a lump on the armpit
- Change in size or shape of the breast
- Dimpling of the skin
- Appearance of a bruise that does not go away
- Inverted nipples
- Breast is warm or hot to the touch
- Blood stained discharge from the nipple
- A rash on the nipple or surrounding area
Causes and Risk Factors for Breast Cancer
- Family History – A faulty gene within your family may increase your risk.
- Age – The risk of breast cancer increases with age. Around 80% of cases are in the over 50’s.
- Previous cases of breast cancer including ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), or atypical lobular hyperplasia (ALH).
- HRT – Hormone Replacement Therapy can increase the risk.
- Radiotherapy – Treatment using radiotherapy can increase the risk of getting breast cancer.
- Dense Breast Tissue – Women who have dense breast tissue may have a higher risk of getting breast cancer due to there being more cells that can become cancerous.
- Weight – Those who are overweight after the menopause has shown to be more at risk.
- Alcohol – Excessive drinking can increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
- Smoking – Smoking increases the chances of getting breast and other forms of cancer.
- Ethnicity – White women are slightly more likely to develop the disease.
Recommended Program for Breast Cancer
For further information on our remote cancer care program, contact us today.